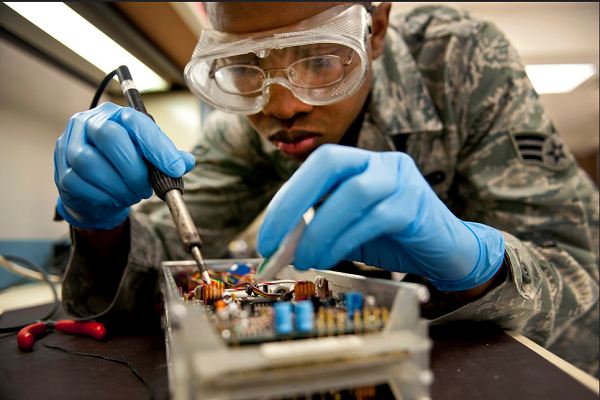
Air Force Precision Measurement Equipment Laboratory (2P0X1) specialist are responsible for calibrating, repairing and modifying, measurement and diagnostic equipment.
These specialist work on equipment used in almost all maintenance activities.
It is their job to ensure the machines work perfectly and only allow for the tiniest fraction of error.
An error in their work could provide catastrophic issues down the road.
Education, Qualifications and Training
This is an entry-level Air Force position with some requirements about general knowledge.
Education
Recruits must have a High School Diploma or GED to enter into this position.
Most positions will require individuals who have a GED to test higher on the ASVAB, versus those with a High School Diploma or GED plus college credits.
Recruits will be required to take and pass the Electronics ASVAB test.
Qualifications
To enter into this position you must be at least 17 years old with parental consent, 18 without, and no older than 39.
You must also have normal colored vision.
Knowledge of electrical, mechanical, physics, optics and thermal principles is also listed on the qualifications summary.
Training
After passing all examinations, individuals will be required to attend Basic Military Training for 8.5 weeks.
Technical School Training will be completed at Keesler Air Force Base for 124 days.
Related Article: 41 Questions To Ask A Military Recruiter
What does a Precision Measurement Equipment Laboratory Specialist do?
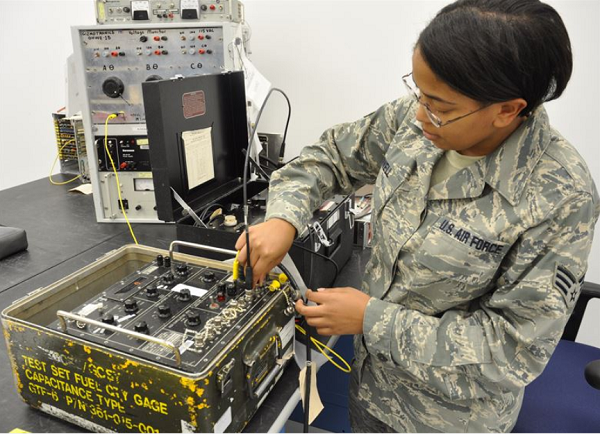

Precision Measurement Equipment Laboratory (PMEL) specialist are the ones who calibrate equipment to measure increments as small as millionths.
Using a variety of tools such as a surface plate, specialist can calibrate tools down to a micro-inch (one millionth of an inch).
They calibrate equipment that runs the different aiming systems, flight systems and any other function.
Most individuals do not think of the large impact the work that these specialist perform can have, until they have not done it correctly.
From early on as an apprentice, these airman are required to inspect, align, troubleshoot and repair all PMEL equipment.
They are required to work on thousands of different types of equipment.
Currently the Air Force has between 3,000 and 4,000 pieces of equipment that these individuals could work on.
As technology advances, this number will increase.
All of these types of equipment will be measured down to fractions.
They work on everything from missile launching to equipment for NASA.
The work that they perform has to be done quickly and efficiently, because if it does not get completed prior to when it is needed, then it could cause detrimental delays.
The test, measurement and diagnostic equipment (TMDE) will be inspected for preventative maintenance.
Specialist will also ensure TMDE meets all cleanliness and safety requirements.
To complete the required maintenance, specialist will use theories of operation, block diagrams, logic trees, schematics and software diagnostics.
All equipment will be calibrated to Air Force Reference Standards.
The PMEL specialist will record and report all maintenance data.
Recording and reporting the data will allow the specialist to prepare technical order improvement and training quality reports.
It also allows the specialist to prepare any special training requests or proposals for modification.
They can use this information to provide training and track any equipment warranty information.
As individuals become Craftsman and Superintendent, they will take on additional responsibilities such as controlling budgets, coordinating mission support requirements and workload responsibilities.
You can view the video below for more information on what it is like to work as a Precision Measurement Lab specialist.
What Does Someone in Precision Measurement Equipment Laboratory get Paid?
As a recruit in an entry-level position with no prior Military experience and no education, individuals can expect to be paid as an E-1.
This pay is roughly around $1600 a month.
All individuals in the Air Force will be paid based off rank and time of service.
As soon as you begin training you will be earning credits towards Electronic Systems Technology.
Earning college credits and a degree will help with your rank and ultimately your pay.
Find more information about Air Force ranks and the pay table here.
Related Article – How Hard Is Air Force Basic Training?
Benefits
The pay included above is outside any other benefits or assistance that airman receive.
Airman are offered insurance, housing allowance and food allowance that greatly offsets that income amount.
The complete list of benefits includes:
- Insurance: Free/Low Cost medical and dental, low-cost life insurance, paid sick time
- Housing: Allowance that covers utilities and maintenance
- Food: Allowance for the on-base dining hall plus tax-free shopping
- Retirement: Available after 20 years
- Vacation: Paid 30 days annually
- Education: Multiple tuition assistance options
- Recreation: On-base facilities and events
For more detailed information on Air Force Benefits read the article here.
Job Reviews
This is a very mentally demanding job.
You must be focused and thinking clearly in order to properly calibrate the equipment.
Positive reviews of the position discuss the great work environment, the work being mentally stimulating and the home-life balance.
Negative reviews included a higher work load to compete with customer demand.
This is a review from a previous PMEL specialist:
You can also review the video below for what the job of a PMEL specialist is like from a PMEL point of view.
Civilian Career Opportunities
Working in this career field will allow airman to gain skills that relate to a job completing calibration as a civilian, or in another related field such as computer science.
Most jobs that relate to calibration and measurement as a civilian will be some form of engineering.
Training with such a wide variety of equipment will allow individuals to go into different fields.
Civilian job titles include:
- Process Engineer
- Test Engineer
- Electromechanical Engineer
- Field Evaluation
Most of these positions are positions that allow for a great home-work life balance while paying in a similar range to a Journeyman or above.

Related Article – Air Force Paralegals: Career Details
Summary
A Precision Measurement Equipment Laboratory (2P0X1) specialist is in charge of calibrating and ensuring accuracy for thousands of Air Force equipment.
These individuals complete the work that often goes unnoticed, but is extremely important.
PMEL specialist will use a variety of different equipment that allows them to calibrate equipment to near perfect measurements.
This is an entry-level position that requires some basic knowledge concepts.
This work is very engaging and can be satisfying.
After your career in the Air Force, experience gained in this field will allow individuals to continue in calibration work, or take a slightly different turn to work with technology or computer sciences.
References:
Air Force Career Field Education and Training Plan
Air Force Academy PMEL Mission
- Replacing Dog Tags: 6 Things You Need to Know - June 28, 2024
- Navy OAR Test Study Guide - June 24, 2024
- 10 Best Sniper Movies of all Time - June 20, 2024
Originally posted on September 24, 2019 @ 4:22 am
Affiliate Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click and purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products I have personally vetted. Learn more.
