The purpose of this article is to provide readers with answers to some of the most common questions asked regarding U.S. Navy Hospital Corpsmen.
What does it take to become a Corpsman in the Navy?
Do Navy Corpsman Go To Boot Camp?
Where / How Long Is A School For Corpsman?
How Much Does A Hospital Corpsman Make?
What Are The Daily Duties Of Corpsman?
1. What does it take to become an HM Corpsman in the Navy?
During the recruiting process, potential members must complete an Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) exam administered while at the Military Entrance Processing Station (MEPS).
Related Article – Navy Jobs List: A List Of All 71 Ratings In The US Navy For 2023
The ASVAB line scores associated with the HM rating is Verbal (VE) which is a combination of Word Knowledge (WK) and Paragraph Comprehension (PC), plus Mathematics Knowledge (MK) and General Science (GS) of 209.
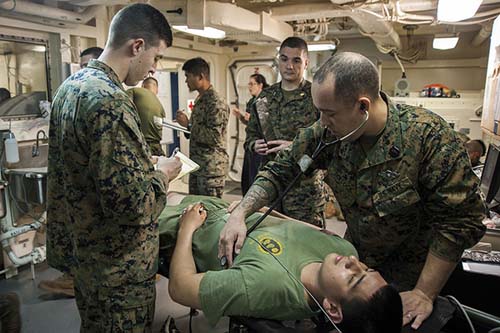
The HM rating is a five-year enlistment commitment. Corpsmen candidates should have outstanding communication skills, good memory, manual dexterity, competence with equipment/machines, and physical stamina. They also need to be dependable and resourceful.
2. Do Navy Corpsman Go To Boot Camp?
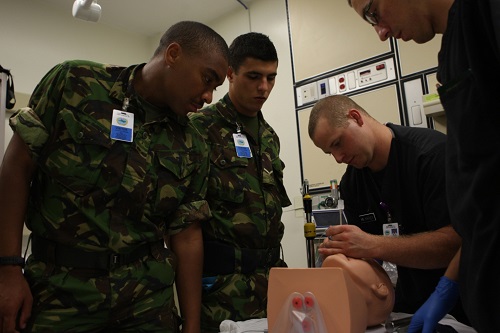
Yes, like all enlisted members, corpsmen begin as new recruits at Recruit Training Command (RTC) in Great Lakes, Illinois.
Related Article – Is Navy Boot Camp Hard?
Boot camp is 10 weeks long and consists of seamanship training, physical conditioning, weapons handling, firefighting, shipboard damage control, water survival, and lessons on Navy core values, customs, and etiquette.
3. Where / How Long Is HM A School?

The Hospital Corpsman Basic Program is the U.S. Navy’s largest A school, located in Joint Base San Antonio, Texas, and is 19 weeks long.
From there, HMs are assigned to an open billet to either a Naval medical facility or an operational Navy or Fleet Marine Force unit. Specialized corpsmen further advance their training at their respective “C” school.
4. How Much Does An HM Hospital Corpsman Make?

Each member serving in the United States Armed Forces is paid the same base pay according to their respective rank.
A Navy corpsman at a pay grade of E-5 would make the same as a Navy master-at-arms at E-5. The military pay charts are updated regularly with a cost of living increase to accommodate that of private sector wage growth.
For 2023, an E-5 with 6 years of service or less makes $3,423 base pay a month.
A new recruit, for example, such as an E-3 with less than 2 years of service, receives $2,259 base pay per month.
Navy Pay Chart for 2023
| Pay Grade | Less than 2 Years | Over 2 Years | Over 3 Years | Over 4 Years | Over 6 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-1 +4 months | $1,917.60 | $1,917.60 | $1,917.60 | $1,917.60 | $1,917.60 |
| E-2 | $2,149.20 | $2,149.20 | $2,149.20 | $2,149.20 | $2,149.20 |
| E-3 | $2,259.90 | $2,402.10 | $2,547.60 | $2,547.60 | $2,547.60 |
| E-4 | $2,503.50 | $2,631.60 | $2,774.10 | $2,914.80 | $3,039.30 |
| E-5 | $2,730.30 | $2,914.20 | $3,055.20 | $3,199.20 | $3,423.90 |
| E-6 | $2,980.50 | $3,279.90 | $3,424.80 | $3,565.50 | $3,711.90 |
| E-7 | $3,445.80 | $3,760.80 | $3,905.10 | $4,095.30 | $4,244.70 |
Related Article: Navy Enlisted And Officer Ranks And Pay
This amount does not include allowances or incentive pay, the most common being Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS) and Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) or Hazardous Duty Incentive Pay (HDIP).
5. What Rank Is a Navy Corpsman?

Every prospective Sailor goes through job classification at MEPS when they decide what career path they want to pursue in the fleet. Navy corpsmen are classified as the HM rating.
At RTC, every recruit begins at the lowest enlisted rank, Seaman Recruit (E-1). The first three ranks (E-1 through E-3) are referred to as apprenticeships and for the HM rate, are designated as Hospitalman Apprentice (HA for E-2) and Hospitalman (HN for E-3).
Once you are promoted to the Petty Officer rates (E-4 through E-6), then your title and role shifts to HM3 through HM1, respectively.
6. What Are The Daily Duties Of a Navy Corpsman (HM)?
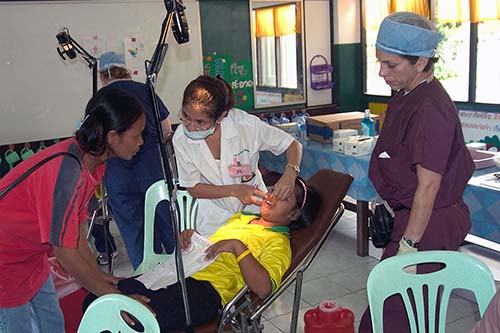
Hospital Corpsmen are responsible for providing medical and dental treatment to their fellow Sailors and Marines and keeping them operational in the fleet.
Corpsmen assist Navy physicians and dentists in surgeries.
Depending on each specialty, the daily duties can vary greatly. These specialties are assigned codes, Navy Enlisted Classification (NEC) codes, and the NEC system supplements the enlisted rating structure.
7. Duties For A HM-0000 Corpsman

A general duty corpsman, HM-0000, assists in the prevention and treatment of disease, injury, and disability, utilizing first aid and preventive medicine; assists in physical examinations; performs general laboratory, pharmacy, and various support services; as do all other specialized trained corpsmen.
There are 38 corpsman NECs.
They can specialize in many areas of medicine, Search and Rescue (SMT), Fleet Marine Force (FMF), Surface Force Independent Duty Corpsman (IDC), Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsman (SARC), Preventive Medicine, Radiology, and Dental Corpsmen, to name a few.
8. Search And Rescue Medical Technician (SMT) Corpsman Duties

HM-8401 SMT Corpsmen support and perform emergency medical care during search and rescue operations. SMT corpsmen transport very sick and injured patients in helicopters and conduct a multitude of casualty and medical evacuations (CASEVAC/MEDEVAC).
Required training to become an SMT corpsman includes successful completion of Naval Aircrew Candidate School, Emergency Medical Technician Ambulance course (EMT-A), qualified in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), triage, intravenous therapy, and having a strong understanding of emergency medical equipment, patient handling, and aeromedical evacuation techniques.
Related Article – Navy Information Systems Technician (IT): Career Details
Additionally, SMT corpsmen must be qualified in the Naval Air Training and Operating Procedures Standardization (NATOPS) program for an assigned aircrew position.
SMT “C” school is located at Pensacola, FL, and is 110 days long.
9. Field Medical Service Technician Duties

HM-8404 Field Medical Service Technicians provide medical care, basic life support, minor surgical procedures, and other routine emergency care for Marines in action and reconnaissance operations.
Corpsmen will attend either Field Medical Training Battalion East (Camp Lejeune, NC) or West (Camp Pendleton, CA) depending on billet openings. During the 8-week course, corpsmen undergo a mix of classroom and field training with an emphasis on field medicine using the principles of Tactical Combat Casualty Care, or TCCC.
Related Article – Navy Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD): Career Details
This course familiarizes Sailors with the Marine Corps organization and procedures. Additionally, training includes individual and small unit tactics, drills, physical conditioning, and weapons handling.
There are no medics in the Marine Corps, and they rely on the Navy to provide administrative, ship transport, and medical for their Marines.
Thus, corpsmen are trained for the battlefield as Fleet Marine Force (FMF) corpsmen.
Typically, a corpsman will hear the term “Green side.” This is in reference to FMF corpsmen working in tandem with Marines, whereas “Blue side” corpsmen generally work in hospitals, clinics, or on ships.
10. Surface Force Independent Duty Corpsman Duties

HM-8425 Surface Force Independent Duty Corpsmen represent the Medical Department aboard surface ships, with FMF units and in isolated duty stations, independent of medical officers.
IDCs perform diagnostic tests, advanced first aid, basic life support, nursing procedures, minor surgery, and basic clinical laboratory procedures, among other routine health care.
They also teach junior medical and nonmedical personnel health education. Surface Force IDC school at the Surface Warfare Medicine Institute (SWMI) in San Diego, CA., and takes one year to complete.
11. Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsmen (SARC) Duties

HM-8427 Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsmen (SARC) work with special operations, specifically Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC) and Marine Corps Special Operations Command (MARSOC).
They are typically found attached to a Marine Recon unit or a United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM) attachment.
They include units such as Navy SEALs, Green Berets, or in some cases even Delta Force.
They use their paramedic skills to provide advanced medical support and emergency medicine.
SARC train to become an operational member of a recon or MARSOC team. They go through an intensive pipeline of training to include dive, parachute, advanced swim, different levels of amphibious and dive medicine qualifications, as well as small and large ammunition training.
SARC has the duty of a hyperbaric chamber operator in which they operate recompression chambers for hyperbaric treatment.
They also perform routine sick calls, diagnostic patient care, logistical duties, minor surgery, suturing, and basic radiology. SARCs know how to set up a Shock Trauma Platoon (STP), Forward Resuscitative Surgery System (FRSS) and can recognize all dive-related ailments.
Sailors wanting to become special amphibious reconnaissance corpsmen may enter the training pipeline from Hospital Corpsman “A” School, by enrolling in the Special Operations Corpsman Program (SOCP).
The course conditions sailors for the lifestyle and training required of candidates applying for SARC, Dive Medical Technician (DMT), and Search and Rescue (SMT) programs.
Candidates must have ASVAB scores of VE+MK+GS >156 or AR+WK>105, or VE+AR+MK+GS>210. The must also have vision correctible to 20/20 and normal color vision.
They also must have passed their last three physical fitness assessments and be able to achieve a first-class swim qualification. Must be able to pass a flight physical and specified specialized parachute physical qualifications.
The massive amount of training requires a minimum of a three-year commitment to serve as a recon corpsman and an enlistment contract of 6 years.
Related Article – Navy Career Counselor (NC): Career Details
12. Preventative Medicine Technician Duties

HM-8432 Preventive Medicine Technicians are corpsmen that assist Medical Department officers in performing Preventive Medicine and Occupational Health Programs for Navy and Marine Corps on and offshore.
They perform inspections of food service, berthing, childcare, and recreational facilities, as well as potable water and waste systems. PMTs conduct bacteriological analysis on various food and water samples and investigate epidemiological sightings.
Additionally, PMTs counsel patients on communicable diseases and administer mass immunization programs.
These corpsmen specialize in all aspects of field sanitation to uphold Navy Occupational Safety and Health standards. PMT school is at Joint Base San Antonio, TX, and is 640 hours.
13. Advanced X-Ray Technician Duties
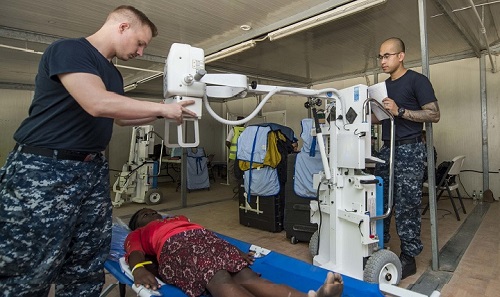
HM-8452 Advanced X-Ray Technicians operate X-ray equipment for diagnostic radiographic exams.
They operate ultrasound equipment, assist the radiologist in fluoroscopic examinations and computerized axial tomographic exams (CAT scans), perform angiography, and process X-ray films. X-ray technicians also maintain quality control and assurance for the equipment.
Advanced X-ray technicians attend “C” school in two phases, phase 1 is completed in Joint Base San Antonio, TX, for 145 days, and phase 2 is in Fort Sam Houston, TX, Portsmouth, VA, or San Diego, CA for 208 days.
14. Dental Assistants Duties
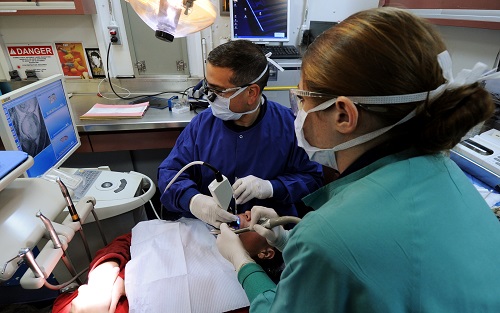
HM-8701 Dental Assistants perform general assistant duties such as dental infection control, management of the dental treatment room, preventive dentistry, assist in comprehensive dental work, and intraoral radiology.
The Navy Dental Assistant course is 40 days long and located in Fort Sam Houston, Texas.
The program provides students with the education and training of entry-level Dental Assistants for fixed and deployable medical facilities.
15. Are Navy Hospital Corpsman Doctors?
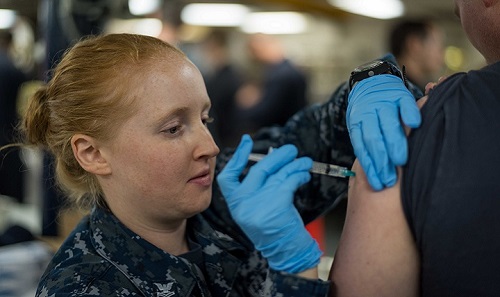
No, corpsmen are not doctors, however, they do assist Navy physicians and dentists.
Corpsmen are enlisted personnel that provide medical support on and offshore. On the battlefield, corpsmen are the first line of medical support for their fellow Sailors and Marines.
Doctors and nurses that join the Navy become commissioned officers.
16. Are Navy Corpsmen Armed?

Hospital corpsmen that deploy with the Marines are FMF corpsmen and are indistinguishable from the rest of the troops, except for the additional medical equipment they carry.
FMF corpsmen carry an M4 and sometimes an M16 like the other Marines. SAR corpsmen carry a .45 or a 9mm.
SARCs have a different variety of weapons: M4 usually modified with an m-grip, a mini desert eagle, or a 9mm and typically a Ka-Bar.
All other corpsmen are considered non-combatants and are not armed. However, all recruits undergo small arms training during boot camp.
Sailors qualify with the M-9 pistol and the Mossberg 500 shotgun.
Conclusion
Being a corpsman in the US Navy is one of the best jobs you can have, both in terms of civilian life as well as Navy life.
If you have any other questions that aren’t addressed in this article, leave a comment below!
Featured Image: wikimedia
- Navy Signing, Enlistment, and Reenlistment Bonuses - June 19, 2024
- Navy Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) Guide - June 19, 2024
- Navy Nurse - June 19, 2024

Spent 4 years as a Corpsman. It set the stage for me for life. I became a nurse and later became a professor of nursing at a university. What a trip its been!!!