In the Submarine Electronics / Computer Field (SECF) of the United States Navy, qualified sailors can train in electronics repair, digital systems, electricity, electronics, computers, and fiber optics for practical use in our country’s nuclear submarine force.
Diligent maintenance and operation of what the Navy calls “Today’s High Technology” digital systems, computers, and advanced electronic equipment used in submarine, sonar, navigation, combat control, and communications are the bread and butter of the four SECF rates.
Related Article – Navy Information Systems Technician (IT): Career Details
Jump To A Section
Training And Career Path
Electronics Technician – Communications(ETR) Details
Electronics Technician – Navigation (ETV) Details
Fire Control Technician (FT) Details
Sonar Technician Submarines (STS) Details
Pay And Benefits for SECF Rates
What’s Life Like for an SECF?
Job Reviews
Civilian Job Opportunities

The SECF rates are:
- ETN (Electronics Technician – Power) – in charge of nuclear propulsion plants, and involved in the maintenance and repair of the nuclear reactor, steam plant, and auxiliary equipment.
- ETV (Electronics Technician – Navigation) – accountable for the operational efficiency of detecting, tracking, and identifying electronic equipment onboard.
- FT (Fire Control Technician) – operates and maintains the combat control systems as well as associated non-tactical computer systems and peripherals.
- STS (Sonar Technician, Submarines) – responsible for the submarine’s sonar mainframe and auxiliary equipment.
SECF volunteers face some steep qualification requirements.
Related Article – Pros and Cons Of Joining The Navy
The training and jobs themselves are both challenging and sometimes stressful.
Only mature young men and women willing to apply themselves and shoulder significant responsibility should apply.
Per the Navy’s Official SECF page:
“The Sailors in the Submarine Electronics Computer Field (SECF) work with a submarine’s sonar, weapons, communications and navigation systems.
The training is rigorous and the career opportunities are equally impressive.”
The active-duty obligation for SECF volunteers is 72 months (six years).
Applicants enlist only for four years but concurrently execute an agreement that extends their obligation for an additional two years.
Related Article – Navy Jobs List: A List Of All 71 Ratings In The Navy
Requirements and Qualifications
As stated earlier, the requirements to qualify for the Navy’s SECF program are high:
- Must be a member of the US Navy.
- You must be a US citizen.
- Must be between the ages of 18 and 41.
- You’ll need normal color perception.
- You must have completed one year of high school algebra
- Must be eligible for a Department of Defense (DoD) security clearance.
You’ll also need to meet the minimum Armed Forces Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) scores as listed below:
- (VE) Verbal Expression + AR (Arithmetic Reasoning) + MK (Mathematics Knowledge) + EI (Electronics Information) + GS (General Science) + Navy Advanced Programs Test (NAPT) = 252, with a minimum of 55 on the NAPT.
- AR + MK + EI (Electronics Information) + GS + NAPT >290, with a minimum of 55 on the NAPT.
- AR + MK + EI + GS > 252
- VE + AR + MK + MC (Mechanical Comprehension) > 252
Training and Career Path
Like all other sailors, SECF volunteers must successfully complete 10 weeks of Navy Recruit Training, at the Recruit Training Command, Great Lakes (RTC Great Lakes).
Related Article: Navy Height And Weight Standards
Basic Enlisted Submarine School
After successful completion of Navy Boot Camp, SECF candidates attend Nuclear Power School (NPS) in Charleston, South Carolina.
Afterward, the SECF candidates are assigned their SECF rate (ETR, ETV, FT, STS) based on their preferences, needs of the Navy, Basic Apprenticeship Training (BAT) scores, and NPS scores.
Class “A” Technical School and Specialty Pipeline School
The SECF Class “A” Technical and Specialty Pipeline Schools for ETNs and ETVs are mostly located in Charleston.
The A School for FTs and STS is in Groton, Connecticut.
However, the duration of training is dependent on the SECF rate:
- ETN & ETV: A School is approximately 6 months long.
- FT & STS: Approximately 4 months
It is here, through group instruction, equipment labs, and practical application that SECF candidates are trained in electronics, basic electricity, and general computer technical knowledge.
Additionally, they learn the communications skills for deployment to a ballistic missile or fast attack submarine.
Let’s take a look at the specific duties of the SECF rates and their lives on a day-to-day basis.
Related Article – Air Force Airborne Mission Systems Operator (1A3X1): Career Details
Electronics Technician – Nuclear Power (ETN)
An Electronics Technician – Nuclear Power (ETN) specializes in the testing, maintenance, and repair of Navy nuclear propulsion systems. ETNs are assigned to multiple submarine classes.
ETNs are charged with repairing, tuning, calibrating, maintaining, and adjusting the nuclear reactor, steam plant, propulsion plant, and auxiliary equipment on the submarine.
At sea, the Electronics Technician monitors the reactor control, alarm warnings, power distribution readings, and airborne particulate radiation detectors.
They maintain and repair electronic and hydraulic-electric systems that support reactor plant operation on both surface and sub-surface ships.
Related Article – Navy Operations Specialist (OS): Career Details

The Sea/Shore rotation for an Electronics Technician – Communication (ETR) is:
| Tour | Sea Tour | Shore Tour |
|---|---|---|
| First Tour | 50 Months | 36 Months |
| Second Tour | 40 Months | 36 Months |
| Third Tour | 40 Months | 36 Months |
| Fourth Tour | 40 Months | 36 Months |
| Fifth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Sixth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Seventh Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
Note that some overseas assignments also count as sea tours.
Electronics Technician – Navigation (ETV)
Electronics Technicians – Navigation (ETV) are deployed to multiple classes of submarines.
The Navy ETV is responsible for electronic equipment utilized for conducting and preparing for basic submarine piloting and navigation.
On a day-to-day basis, the Electronics Technician – Navigation (ETV) monitors and operates the Global Positioning and Inertial Navigation systems under the supervision of senior personnel.
ETVs are also responsible for maintaining the ship control subsystems as well as atmosphere monitoring systems. They maintain, repair, and calibrate electronic equipment used for navigation.

Related Article – Marine Corps Electrical Engineer (MOS 1142): Career Details
The Sea/Shore rotation for an Electronics Technician – Navigation (ETV) is:
| Tour | Sea Tour | Shore Tour |
|---|---|---|
| First Tour | 48 Months | 36 Months |
| Second Tour | 42 Months | 36 Months |
| Third Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Fourth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Fifth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Sixth Tour | 36 Months | 36 36 Months |
| Seventh Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
Note that some overseas assignments may also count as sea tours.
Fire Control Technician (FT)
Fire Control Technicians (FT) are specialized in combat systems and deploy aboard multiple classes of submarines.
They have the responsibility of operating and maintaining advanced electronic equipment utilized in the submarine weapon systems, in regards to underwater weapons and guided-missile systems.

Related Article – Navy Hull Technician (HT): Career Details
On a day-to-day basis, Fire Control Technicians (FT) perform testing of the submarine combat control systems.
They also maintain and operate non-tactical computer systems and are involved in weapons-handling functions as well.
The Sea/Shore rotation for a Fire Control Technician (FT) is:
| Tour | Sea Tour | Shore Tour |
|---|---|---|
| First Tour | 54 Months | 36 Months |
| Second Tour | 42 Months | 36 Months |
| Third Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Fourth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Fifth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Sixth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Seventh Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
Note that some overseas assignments count as sea tours.
Related Article – US Navy Aviation Electronics Technician (AT): Career Profile
Sonar Technician Submarines (STS)
Sonar Technician Submarines (STS) are specialized in sonar systems and deploy aboard multiple classes of submarines.
They’re responsible for operating and maintaining advanced electronic equipment utilized in the submarine sonar systems.
On a day-to-day basis, Sonar Technicians Submarines (STS) perform testing of scientific data collection and underwater surveillance systems.
They also calibrate, adjust, and repair electronic equipment utilized for scientific data collection.
They may also test and repair combat control systems associated with sonar systems.

The Sea/Shore rotation for a Sonar Technician Submarine (STS) is:
| Tour | Sea Tour | Shore Tour |
|---|---|---|
| First Tour | 48 Months | 36 Months |
| Second Tour | 48 Months | 36 Months |
| Third Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Fourth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Fifth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Sixth Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
| Seventh Tour | 36 Months | 36 Months |
Note that some overseas assignments count as sea tours.
How Much Are Navy SECF Sailors Paid?
Like the other Armed Services, the Navy bases a sailor’s pay on their rank and length of service.
| Insignia | Pay Grade | Rank | Abbreviation | 2023 Minimum Monthly Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | E-1 +4 months | Seaman Recruit | SR | $1,917.60 |
| E-2 | Seaman Apprentice | SA | $2,149.20 | |
| E-3 | Seaman | SN | $2,259.90 | |
| E-4 | Petty Officer Third Class | PO3 | $2,503.50 | |
| E-5 | Petty Officer Second Class | PO2 | $2,730.30 | |
| E-6 | Petty Officer First Class | PO1 | $2,980.50 | |
| E-7 | Chief Petty Officer | CPO | $3,445.80 | |
| E-8 | Senior Chief Petty Officer | SCPO | $4,957.20 | |
| E-9 | Master Chief Petty Officer | MCPO | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Command Master Chief Petty Officer | CMDCM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Master Chief Petty Officer Of The Navy | MCPON | $6,055.50 |
All sailors may be entitled to other forms of compensation including Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH), Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS), and billet pay (sea pay, submarine pay, hazardous duty pay, etc.) if eligible.
Rates in the SECF program are often eligible for enlistment and reenlistment bonuses dependant on the current needs of the Navy.
What’s Life Like for Sailors SECF Rates
As stated earlier, life as an SECF Sailor is challenging and, at times, stressful.
There is much time spent at sea aboard the submarine, and the hours are long.
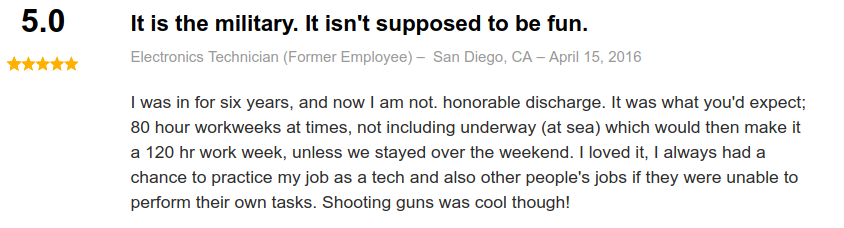
One reviewer claimed an average of 120-hour work weeks, adding “I loved it.”
Sailors in the SECF rate will be required to obtain their Submarine Warfare Specialist Pin (SS).
The SS Pin is earned through qualification and broken down into qualification blocks or phases.
These include:
- Indoctrination/Damage Control Phase
- Propulsion Phase
- Auxiliary Systems Phase
- Electronic Equipment and Navigation Phase
- Combat Systems Phase
After successful completion of the qualification card/book, the sailor must face a “Qual Board” comprised of a submarine-qualified officer, a chief petty officer, and a petty officer who “drill” the member with questions concerning the different systems on the shift, often asking them to draw and/or explain these systems.
If the board deems the sailor worthy, they recommend the SS qualification to the Commanding Officer.
If the CO agrees with the board’s recommendation, the Sailor is presented with their SS qualification, and their service jacket is updated to reflect such.
Their CO presents their Submarine Warfare Specialist Pin (SS), or “Dolphins,” so they can wear it on their uniform and use the SS after their rate (i.e., STS2(SS), or FT1(SS).
SS-qualified sailors are designated as “Qualified in Submarines” and are viewed with respect by their fellow sailors.
Related Article: 10 Best Jobs In The Navy For Civilian Life
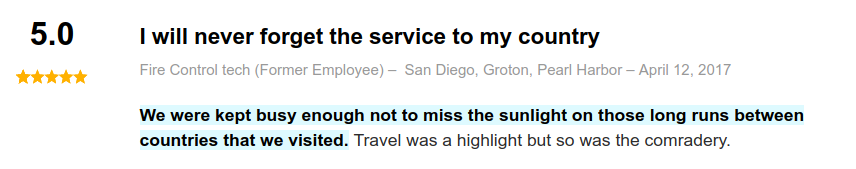
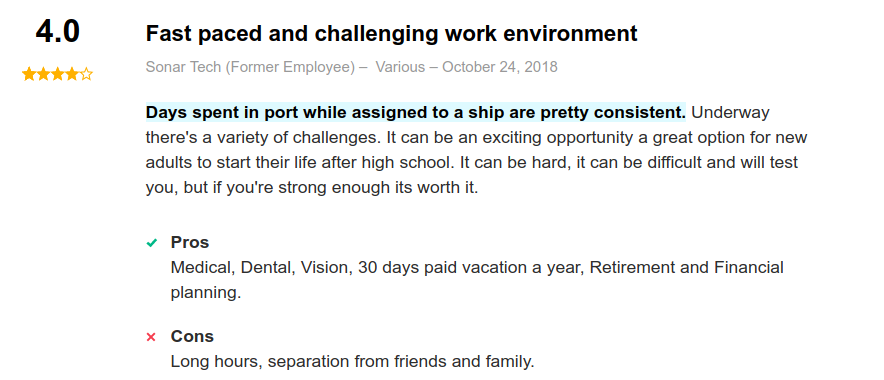
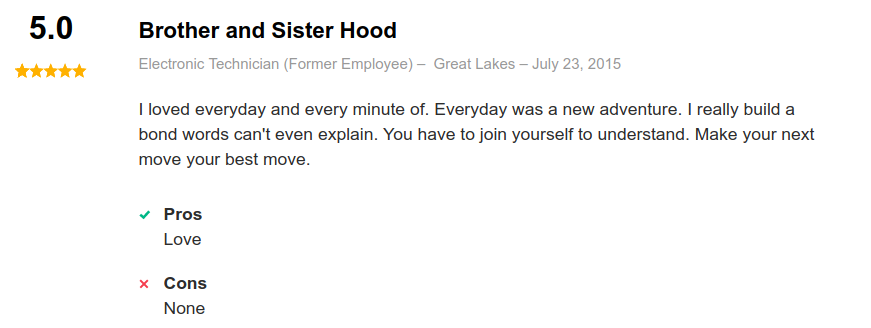
Job Reviews
Moreover, reviews on indeed.com are primarily positive:

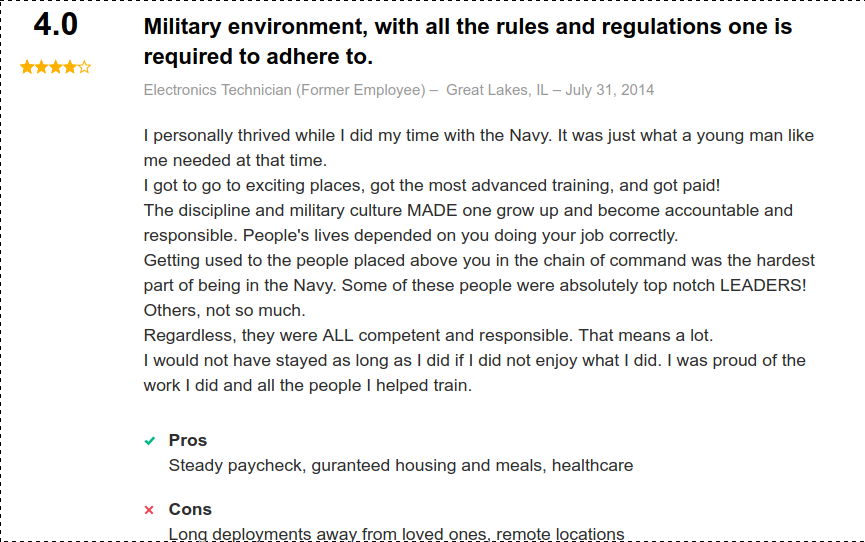
Civilian Career Opportunities
Civilian career opportunities abound for SECF Sailors and include such jobs as:
- Electrical/Electronic Technicians
- Electro-Mechanical Technicians
- Radio Operators
- Electrical Engineering Technicians
- Computer Operators
- Electronics Engineers
Sailors in the SCEF Program should take full advantage of on-the-job training (OJT) opportunities, and educational opportunities offered and afforded them during their naval service.
Related Article – Dishonorable Discharge: Reasons, Consequences, And More
The United States Military Apprenticeship Program (USMAP) also allows them to complete their civilian apprenticeship requirements while on active duty.
Several national certifications, federal licenses, state licenses, and apprenticeships are available for departing ETNs, ETVs, FTs, and STSs.
If you are considering the US Navy, can meet the rigid qualifications, have the maturity required, and feel confident in handling the training, long hours, and life aboard a submarine, a career in the Navy Submarine Electronics / Computer Field could just be for you.
References
Official Navy Submarine Electronics Careers Description
Navy Personnel Command Submarine Electronics Computer Field Overview
U.S. Navy COOL Summary For Fire Control Technician (FT)
Navy COOL Summary For Navy Electronics Technician, Submarine, Communications (ETR)
U.S. Navy COOL Summary For Navy Electronics Technician, Submarine, Navigation (ETV)
Navy COOL Summary For Navy Sonar Technician Submarine (STS)
U.S. Navy Fire Control Technician (FC) Reviews
U.S. Navy Electronics Technician (ETR/ETV) Reviews
Navy Sonar Technician (STS) Reviews
- Gas Turbine Systems Technician (GSM and GSE): Career Details - June 18, 2024
- Interior Communications Electrician (IC): 2023 Career Details - June 18, 2024
- Religious Program Specialist (RP): 2023 Career Details - June 18, 2024
General FAQ
What is SECF in the Navy?
SECF stands for Submarine Electronics / Computer Field (SECF) in the U.S. Navy, and includes electronics repair, digital systems, electricity, electronics, computers, and fiber optics for the Navy nuclear submarine force.
What are the SECF jobs in the Navy?
The SCEF rates include Electronics Technician – Communications, Electronics Technician – Navigation, Fire Control Technician, and Sonar Technician.
How much is sub pay in the Navy?
Sub pay for enlisted Navy personnel is based on rank and time in service and can range from $75 per month to $425 per month.
How long is A School for Navy SECF rates?
A School for SECF technicians ranges according to complexity of the systems and can last as short as 23 weeks for Communications and Navigation techs up to 37 seeks for Sonar technicians.
How do you become an SECF tech in the Navy?
To qualify in SECF, you’ll need a combined ASVAB score of 222 for Arithmetic, Math, Electronics, and General Science or Verbal, Arithmetic, Math, and Mechanical Comprehension. You’ll need normal hearing and color perception and must be a U.S. citizen.
Originally posted on August 19, 2019 @ 3:27 pm
Affiliate Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click and purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products I have personally vetted. Learn more.
